Silicon Valley Bank Collapse Explained
There seems to be a general confusion/misunderstanding among folks relating to the Silicon Valley Bank (SVB) collapse, so
thought would explain in very simple terms for the benefit of others.
But, before we get started, let us make sure we are all on the same page with respect to few important financial terms, such
as, Bonds, Inflation, and Interest
Rates.
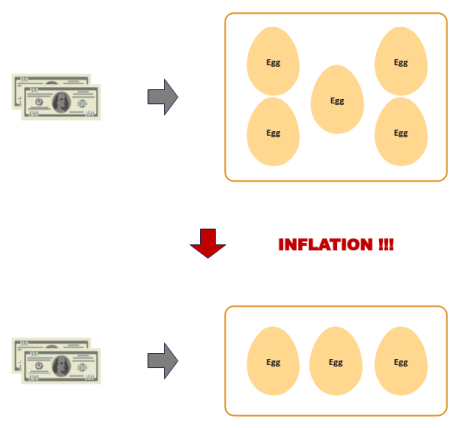
Inflation is the gradual decline in the purchasing power (value) of a currency with an increase
in the prices of goods and services over time.
Inflation occurs due to various factors, such as, the government printing more money (increased
money supply), increase in manufacturing costs, or supply-demand issues (meaning more demand and less supply).
In order to curtail Inflation, the government typically raises the Interest
Rates. This implies it becomes more expensive to borrow money to spend, which leads to consumers spending less and
thereby forcing the prices to go lower.
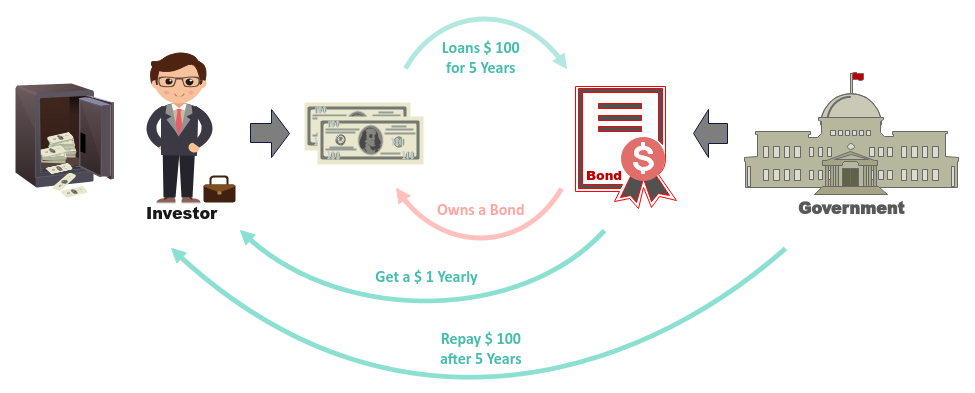
When Governments want to undertake major projects or pay for services, they need to raise Capital.
This is done by collecting Taxes and by issuing Bonds.
On the other hand, we have investors with money, which they wish to grow, rather than keeping it under their bed. They can
either invest by buying Bonds or Stocks.
Bonds are generally considered to be a less risky an investment than Stocks
.
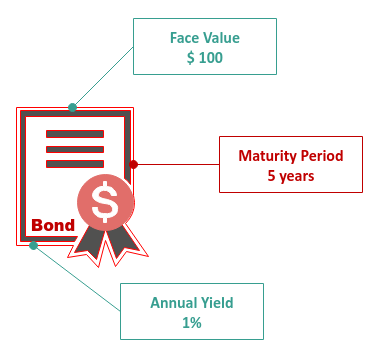
Investors loan their hard-earned money (Principal) to the Government for a fixed period of
time (Maturity period) by investing in Bonds (with a certain value
Face Value) in exchange for a fixed rate of return each year (Yield
). At the end of the Maturity period, the Government will return the original loan
Principal back to the investor.
The Government will issue an interest amount equal to the Yield of the Bond
to the investor at a fixed interval period, say, Yearly.
In early 2020, the WORLD got hit by COVID. In addition, the
Interest Rate was close to ZERO. The end result - manufacturing
came to a stand-still, creating a shortage of essential goods, while there was an abundance of money to spend. A perfect
storm for INFLATION.
In order to tame the inflation, the government started to raise the Interest
Rates from early 2022.
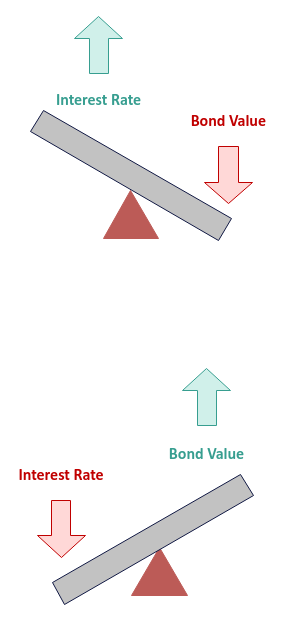
Interestingly, when the Interest Rates go UP, the Face Value of a
Bond goes DOWN and vice versa.
For example, assume the current Interest Rate is 1% and the Face Value
of a Bond is $ 100. This means an investor will get $1 at the end of each year till the
Maturity period. When the Interest Rate goes up to 2%, any new
Bond issued will carry a Yield of 2%. That is, an investor will get $2
at the end of each year till the Maturity period. This implies new investors will naturally be
MORE interested in the Bond with a 2% Yield
versus a Bond with a 1% Yield.
If an investor, who owns a Bond with a 1% Yield, falls on hard times
and desparately needs money, they will have to sell the Bond at a lower Face
Value of $ 95 in order for it to be attractive for another buyer.
With the financial BASICS at hand, we are now ready to understand the situation ...
Silicon Valley Bank (SVB for short) was a regional bank in the West Coast catering to the banking needs of start-ups. At
the end of 2019, SVB had deposits of about $ 60 Billion.
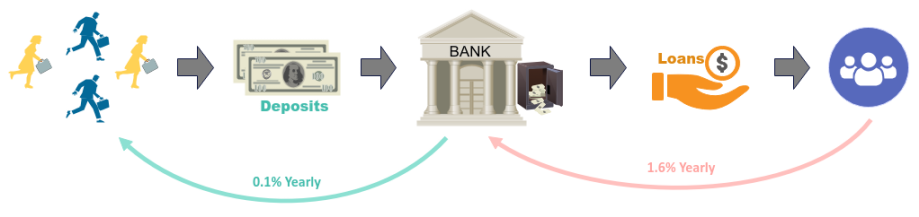
Banks typically pay a very low Interest Rate on deposits, say, 0.1%. In turn, the bank uses the
customer deposits to make loan offers to other customers who are in need of money and willing to pay a higher
Interest Rate, say, 1.6%. The bank nets the profit of 1.5% from the interest earned on the loans.
This is one of the ways the bank makes money.
When COVID hit in early 2020, there was a boom in new start-ups with an abundant supply of money
from investors. As as result, there was a sudden influx of more new deposits coming into SVB. Just to get a sense, at the
end of 2022, SVB had deposits of about $ 180 Billion.
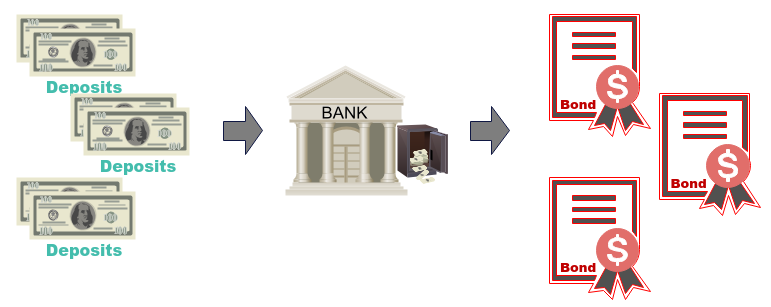
SVB could not make loans offers faster to other customers, so SVB decided to invest a significant amount of those deposits
in government Bonds. Remember that the Interest Rates were close to
ZERO till the early 2022.
When the government started to raise the Interest Rates in 2022, the start-ups began to feel the
pain due to higher costs for goods and services. As a result, they started to tap into their deposits in SVB and began to
make withdrawals from their deposits at SVB. In addition, the customers also wanted to take advantage of the raising
Interest Rates situation and began to withdraw money from SVB for investment elsewhere.
Remember that SVB had locked up its deposits in long-term government Bonds. In order to create
liquidity, SVB was forced to sell some of their government Bonds at a loss. SVB had incurred a
loss of about $ 2 Billion at the beginning of 2023.
When SVB came out in early Mar 2023 and indicated it needs to raise capital, it created a panic amongst customers, which
resulted in more withdrawals, ultimately causing SVB to COLLAPSE !!!